

This service could again take the form of military service (typical in the case of a knight) or, as tenants might be of a lower social class (but still be freemen) and they might not have had the necessary military skills or equipment, more usually they offered a percentage of their revenue from the land they rented (either in money or produce) or, later in the Middle Ages, made a fixed payment of rent. Once again, the person was given the right to use and profit from this land and in return, in one form or another, then owed a service to the landowner. The nobles who had received land, often called suzerain vassals, could have much more than they either needed or could manage themselves and so they often sub-let parts of it to tenant vassals. The feudal system proper became widespread in Western Europe from the 11th century CE onwards, largely thanks to the Normans as their rulers carved up and dished out lands wherever their armies conquered. The system had its roots in the Roman manorial system (in which workers were compensated with protection while living on large estates) and in the 8th century CE kingdom of the Franks where a king gave out land for life ( benefice) to reward loyal nobles and receive service in return.

The fee signified the land given (the fief) as a payment for regular military service. The word ‘feudalism’ derives from the medieval Latin terms feudalis, meaning fee, and feodum, meaning fief.

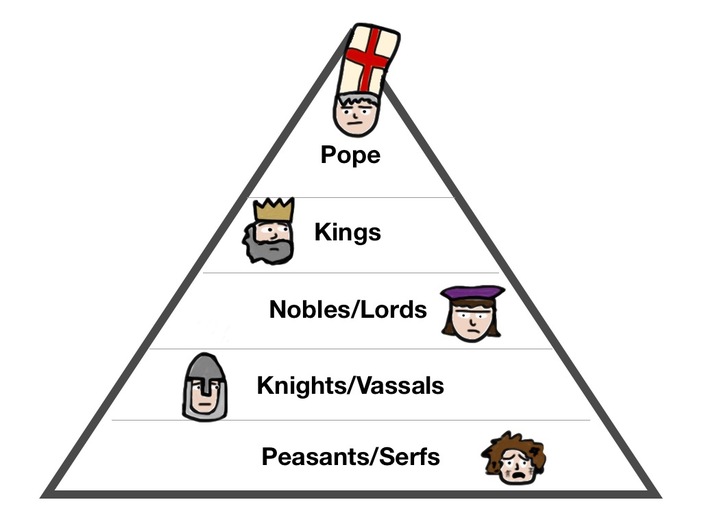
The dominant social system in medieval Europe, in which the nobility held lands from the Crown in exchange for military service, and vassals were in turn tenants of the nobles, while the peasants (villeins or serfs) were obliged to live on their lord's land and give him homage, labour, and a share of the produce, notionally in exchange for military protection. The Oxford English Dictionary has as concise a definition for feudalism as anywhere while still including its various levels of application: As a consequence, many historians beleive that the term feudalism is only of limited use in understanding medieval societies. Neither can the feudal system, once defined, be applied uniformly across different European states as there were variations in laws and customs in different geographical areas and in different centuries. The term feudalism was not used by the people who lived in the Middle Ages. The terms were applied to European medieval society from the 16th century CE onwards and subsequently to societies elsewhere, notably in the Zhou period of China (1046-256 BCE) and Edo period of Japan (1603-1868 CE). Born November 7, l998 in Cartersville, Georgia, Max spent his early childhood years in Augusta, where he met his closest friends and made cherished memories.Īlthough the term ‘feudalism’ and ‘feudal society’ are commonly used in history texts, scholars have never agreed on precisely what those terms mean. Use your vocabulary lists and include ALL the relevant people. Assignment prompt: “Create a pyramid chart showing the feudalism hierarchy of the Middle Ages.” Using page 188 in your textbooks and the handout “Who was who in the Middle Ages,” create a pyramid chart showing the feudalism hierarchy of the Middle Ages. In this power structure, the power of an individual was directly tied with the amount of land he held. Problems of Definitionįeudal System What was the feudal system? The Feudal system was a power structure which existed primarily during the medieval times in Europe. Both lord and vassal were freemen and the term feudalism is not generally applied to the relationship between the unfree peasantry (serfs or villeins) and the person of higher social rank on whose land they laboured. Such payment came in the form of feudal service which could mean military service or the regular payment of produce or money. A landowner (lord) gave a fief, along with a promise of military and legal protection, in return for a payment of some kind from the person who received it (vassal). Feudalism was the system in European medieval societies of the 10th to 13th centuries CE whereby a social hierarchy was established based on local administrative control and the distribution of land into units (fiefs).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
